We may receive compensation from partners & advertisers. Read our disclosure for details.
A $0 deductible health insurance plan eliminates the need for any out-of-pocket expenses before your insurance coverage kicks in.
Essentially, a zero dollar deductible plan begins covering your costs immediately, without you having to fulfill or “meet” the requirement.
Financially, having no deductible works in your favor if you need a procedure done sooner rather than later. However, there are pros and cons of zero deductible health insurance you should consider, so keep reading.
We put together this brief guide to help explain $0 and low deductibles, high deductibles, and premiums as well as ways to manage those expenses and keep more money in your pocket!
This article refers to Marketplace health insurance. To learn more about coinsurance, out-of-pocket maximums and metal levels visit our Health page or contact us for more information!
In This Article:
What Is Open Enrollment?
Open Enrollment, which runs from November 1st to January 15th for individual ACA Marketplace Health Plans is your opportunity to enroll or make changes to your coverage.
Outside of that period, you may be eligible for a Special Enrollment Period if you experience certain life events, such as loss of coverage, getting married, adopting a child, or a change in household size.
The ACA Marketplace
Healthare.gov is the official Marketplace for health plans, but some states manage their own exchange.
For example, Maryland residents have to go through Maryland Health Connection, Virginia has Virginia’s Insurance Marketplace and Pennsylvania residents would use Pennie for ACA health insurance.
$0 Deductible Health Insurance vs High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP)?
Choosing the best health insurance plan can be a complicated task with all the options available, but once you know how it all fits together you’ll just have to crunch the numbers.
You’ll come across a range of plans: zero deductible, low deductible, high deductible health plans (HDHPs) and plans somewhere in the middle.
Health insurance deductibles represent the amount of money you’re responsible for paying out-of-pocket before your health insurance coverage begins.
The Trade-Off: Deductibles and premiums often follow an inverse relationship. In other words, a plan with a low deductible generally has a higher monthly payment (the premium), while high-deductible plans typically offer lower monthly premiums.
This is one of the most important things to consider when it comes to health insurance. You’re individual needs, health and financial situation all play a role.
The IRS sets the limits each year:
For 2024 your plan is a high deductible health plan (HDHP) if the deductible is more than $1,600 or your family plan is more than $3,200.
Deductible amounts vary across plans and insurance companies, but they can range anywhere from $0 to $7,000 or more per person, depending on the kind of coverage you select.
A downside to a high deductible plan is skipping doctor visits & treatments altogether to avoid the large out-of-pocket expense.
For many Americans, having to come up with $2,000-$5,000 to meet the deductible on short notice may be a challenge.
$0 Deductible Health Insurance: Good or Bad?
Purchasing health insurance with a zero $0 deductible can be beneficial if you want to limit your out-of-pocket expenses sooner or each time you see the doctor. Meaning, it’s a good choice if you have a scheduled or out-patient procedure coming up.
These low-deductible health plans will cost more each month, but federal tax credits can help reduce the premium you pay each month if you qualify.
You’ll know the amount of any tax credit when you fill out an application.
If you have some health issues and think you’ll need to visit the doctor a few times a year a zero deductible or lower deductible plan could be a better solution.
Just be mindful of the monthly premium and how it relates to your other obligations. Some households may find themselves having to decide between health insurance and household bills when money is tight.
On the other hand, a high deductible plan will typically cost you less each month, but more when you need to use it.
While this may seem like a big deal, it can save you money in the long run if you’re healthy and don’t require frequent medical visits.
Going this route takes some financial planning though. Remember, deductibles need to be paid first, and having to come up with a lump sum can be stressful.
Zero Deductible Health Insurance: PROS
The biggest advantage of $0 deductible health insurance is that you won’t have to pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. This can be especially beneficial if you have a chronic condition or require frequent medical care.
Low or zero deductible health insurance can be a great way to save money on healthcare costs, but it’s important to keep in mind that you’ll still need to budget for higher monthly premiums and other out-of-pocket expenses.
By planning and setting aside funds for healthcare, you can ensure that you’re able to maintain an active policy and get the care you need when you need it.
Zero Deductible Health Insurance: CONS
While $0 deductible health insurance may seem like a good option, there are some potential downsides to consider. First, these plans can often have higher overall costs, including higher monthly premiums and coinsurance.
Additionally, some $0 deductible plans may have limited provider networks, meaning you may not have access to the doctors and specialists you need. Compare plans carefully.
Finally, with a low or zero deductible plan you won’t be able to take advantage of a Health Savings Account which are set aside for HDHPs.
How Metal Levels Work
There are four different metal levels of coverage. These metals, determined by the Health Insurance Marketplace, signify the different payouts associated with each plan.
Bronze level plans payout 60/40 (60% paid by insurance, 40% paid by consumer). Silver plans payout 70/30.
Gold plans payout 80/20 and Platinum plans have a 90/10 payout. Typically, higher payouts from the insurance company mean higher monthly premiums. Lower deductible plans are usually in these metal levels.
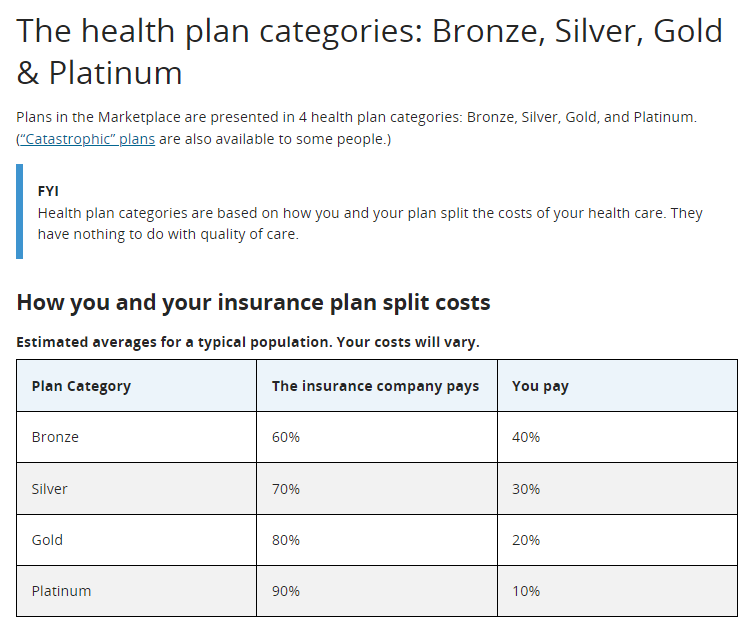
Source: Healthcare.gov
Example: Gold Plan with a $5,000 deductible
Let’s say you need to schedule a procedure. Surgery, hospital stay and physical therapy total $15,000.
Your first obligation is the $5,000 deductible which leaves you with a hospital bill of $10,000.
With your Gold Plan you share the bill with the insurance company 80/20 which is $2,000.
Your total out-of-pocket cost for this accident: $5,000 + $2,000 = $7,000.
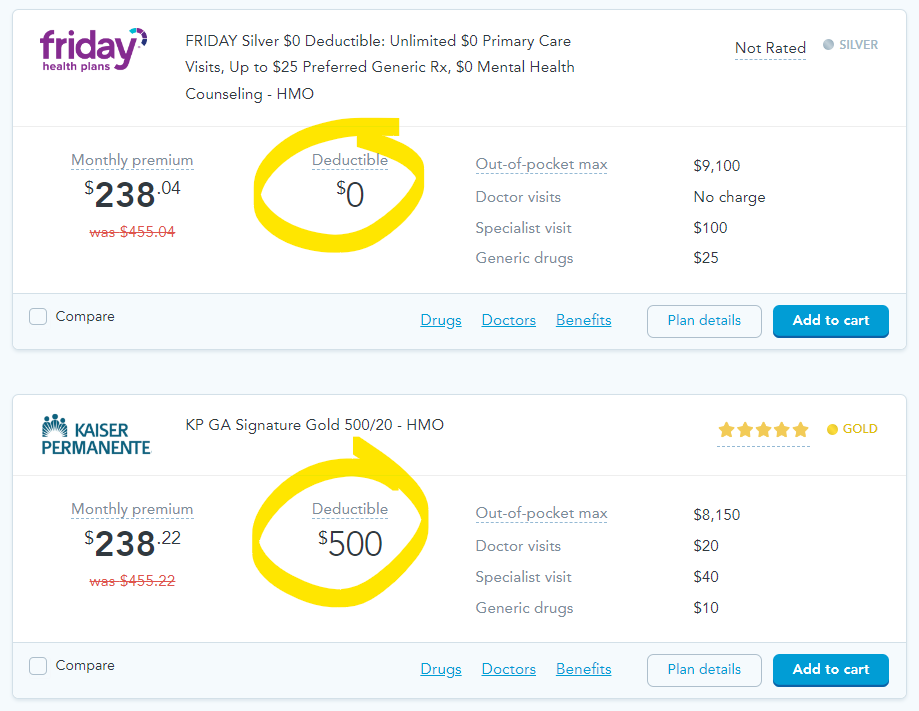
Example: Zero dollar deductible vs. $500 deductible
At first glance, the Silver plan below isn’t all that bad with a $238 a month premium after tax credits. The plan will pay 70% of covered events with a $0 deductible. You’ll be responsible for the remaining 30% up to $9,100 — the out-of-pocket max. After that, the insurance company will pay 100% of your bills for the rest of the year.
On the other hand, the Gold plan has the same $238 a month premium, a $500 deductible but a lower out-of-pocket max of $8,150.
Looking at examples below, see how higher deductibles compare with lower monthly premiums and lower costs for prescriptions.
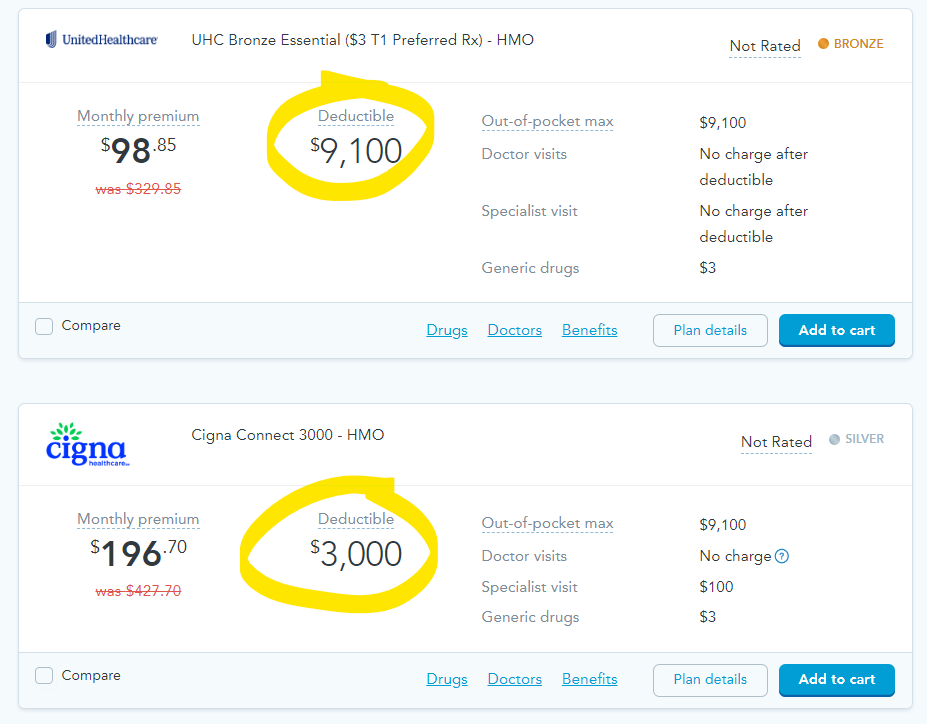
Whatever you choose will ultimately depend on your health, family and finances. Our suggestion is to budget and have a plan to avoid financial hardship down the road.
Choose A Silver Plan – If You Can
Tax credits are one way to make health insurance more affordable. Cost-sharing reductions (CSRs) take it a step further by helping to reduce or limit the related expenses of health insurance like deductibles.
CSR’s are based on income and are only available with Silver Plans.
If you’re young, healthy, and rarely see a doctor the lower monthly premiums of a Bronze Plan (with higher deductibles) can potentially save you a lot of money upfront.
On the other hand, if you have children higher deductibles might not be ideal since you are likely to visit the pediatrician a lot (I can relate to this one!)
Also, higher deductible plans may not be the best idea if you have a pre-existing or chronic condition and you need to use your plan frequently.
A Silver plan strikes a good balance between high deductible plans and low or zero deductible health insurance.
Compare $0 Deductible Health Insurance Plans
Shopping and comparing health insurance plans from an ACA Marketplace can seem intimidating, but there are several user-friendly platforms. You can start at Healthcare.gov to learn more.
Remember, during Open Enrollment you can sign up for coverage. Outside of that, you’ll have to qualify for a Special Enrollment Period.

How To Manage Health Insurance Costs
Once you choose a plan, you’ll want to manage it financially. This can be a challenge, especially when it comes to deductibles and premiums.
Note: Be sure to consult with a financial planner or tax professional as needed to fully understand your options.
If you’re not paying a high deductible, you’re most likely paying a high premium.
And some other expenses to consider are your coinsurance — which is the amount of the bill you share with the insurance company, and out-of-pocket maximum
Taking control of your finances and having an emergency fund is smart financial planning. There are several ways to manage these costs and to better prepare for unexpected bills.
High deductible health plans (HDHPs) have become increasingly popular in recent years as a way to lower monthly premiums. However, these plans can have out-of-pocket expenses that can be a challenge.
Remember in our earlier example, that $5,000 deductible needs to be paid before the plan starts to share any costs. Supplemental health insurance can help with that.
Another solution is an HSA or health savings account which allows you to set aside pre-tax dollars for medical expenses. More below.
Supplemental Health Insurance
Supplemental plans can help cover the cost of your deductible and other out-of-pocket expenses, such as copays and coinsurance with lump sum cash benefits.
If you’re injured or become ill, a supplemental plan like Accident Insurance or Critical Illness can provide you with a lump-sum payment to help pay for your related expenses.
UnitedHealthcare and Aetna offer supplemental insurance to add a level of protection against healthcare costs that may go beyond the scope of your health plan.
You have the flexibility and financial freedom to use the money however you choose.
Learn more in Supplemental >>

Health Savings Account (HSA)
A health savings account (HSA) makes sense if you have an HDHP.
You open an account, make contributions, invest and get tax-free growth and tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses.
Fidelity

Lively
Important: An HSA Is Not For Everyone
If you have the means, an HSA can be very useful to help manage high deductibles and medical expenses. It can also be a smart investment tool for retirement.
Conversely, if you don’t have the extra money to set aside each month or take advantage of the investing features of an HSA you might want to stick with a traditional savings account or some other option.
That way, if a non-medical emergency comes up you’ll have access to your funds without penalty.
Note: Be sure to consult with a financial planner or tax professional as needed to fully understand your options.
ON YOUTUBE

Don’t Use Your Credit Cards!
The whole point of financial security is having resources in place and avoiding debt. If you’re faced with large medical expenses and not much cash you might be tempted to charge it.
You’ve probably heard the Fed is raising rates like crazy to curb inflation which will have a huge impact on how much you owe the credit card company each month.
Even if you have to borrow from a friend or work something out with the hospital do what you can to avoid using plastic.
Is $0 Deductible Health Insurance Good or Bad?
Having a zero deductible health insurance plan is a good thing, but at what cost?
Yes, it eliminates the need for you to meet a deductible before your medical expenses are covered. This makes sense if you anticipate frequent medical needs and want to avoid upfront out-of-pocket costs.
However, plans with no deductibles tend to have higher monthly premiums. This means you’ll have to weigh the immediate financial relief against the cost of higher premiums. Try and strike a balance that aligns with your health and your bank account.
Information is meant to be accurate and educational and not intended to be legal, medical or financial advice. Be sure to do your own research and contact a professional for help. Our site is free to use, but we may receive a commission from our partners & advertisers at no additional cost to you. Read our disclosure for more information.